Primary Packaging vs Secondary Packaging vs Tertiary Packaging – What’s the Difference?
Waqas Khan Pitafi 2025-05-09 10:26:52
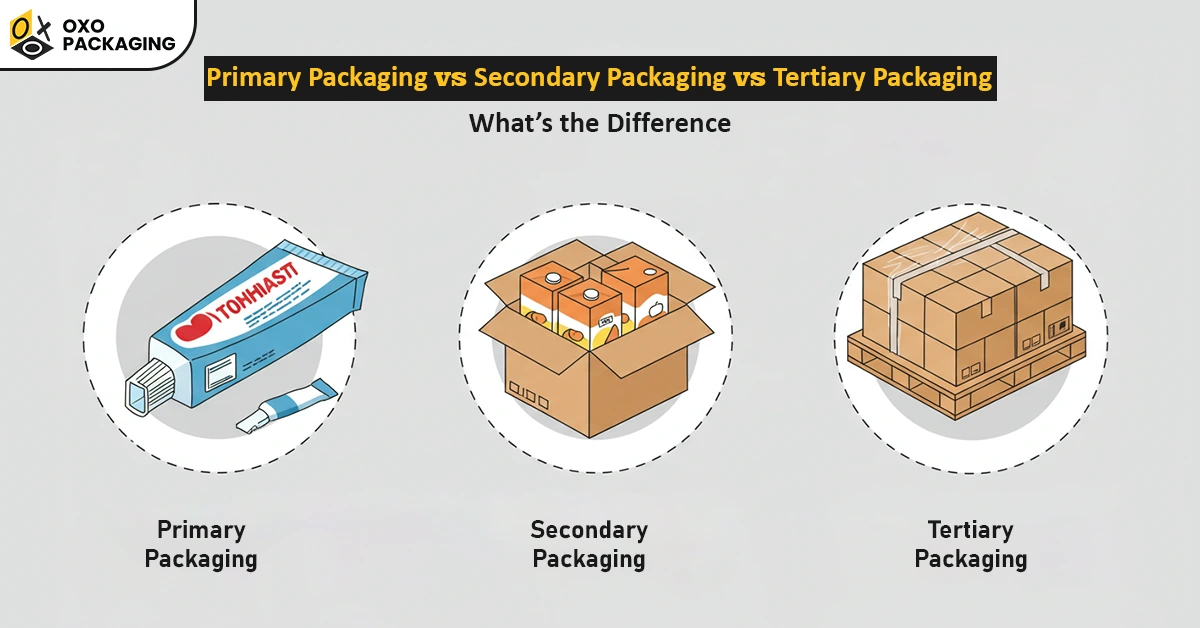
Packaging plays a crucial role in the protection of warehouse products, from secure wrapping to easy assembly and efficient storage. In the packaging industry, there are three main levels of packaging, each featuring unique characteristics and storage functions.
Primary, secondary, and tertiary are those packaging levels that are important to deliver products securely and promote the overall efficiency of your shipping processes. Read this blog to explore the characteristics and considerations of each packaging level to make a well-informed choice for your business.
Why Packaging Plays a Crucial Role In Supply Chain?
Whether you are a retail or e-commerce brand, packaging is the only way for your business to ensure safe shipping from the manufacturer to customers. Choosing the right packaging not only provides a cushioning effect to protect the product during shipping. Instead, it also serves as a powerful marketing tool by highlighting your product features.
Multiple layers of packaging safeguard the product and ensure it reaches its final destination safely and in pristine condition while minimising the risk of damage. In this regard, packaging refers to specific elements that protect and assemble products for transportation, storage, and handling.
While products are prone to a series of potential risks that packaging must reduce during supply chain processes. Harsh environmental conditions like extreme temperatures or humidity, handling errors including scratches or crushes, and storage deterioration like corrosion or erosion are among those risks.
However, these potential risks may vary significantly depending on the type of load storage, especially in the case of chemical storage. To sum up, effective packaging facilitates the main storage functions in the supply chain as follows:
- Serve as a shield for protecting items in all stages of the supply chain
- Streamline the handling of products with compatible stacking
- Communicate the characteristics of products to ensure their proper handling
- Promote the brand image, particularly in the case of commerce companies
Why are Different Levels of Packaging Important?
Whether your business is shipping similar items in a large group for retail display or individual items for customer usage, packaging levels at every stage are crucial. On the primary packaging level, customers see the product directly with basic protection, essential brand information, and retail appeal.
Coming to secondary packaging, it offers extra protection to grouped units of primary packaging during transportation and shipping. Secondary packaging level helps to enhance the overall brand image by highlighting your logo and graphics with a distinctive look.
Last but not least, tertiary packaging doesn’t allow customers to see products directly. But it does not imply you should overlook this packaging level. Regardless of the fact consumer-facing products or not, a smart strategy is involved.
And tertiary packaging keeps your products in bulk safe during shipping and handling. Secure shipping of bulk products is just as important as grabbing the attention of customers on crowded retail shelves. However, every business wants to save money while protecting its items.
The fun fact is that working with an experienced and reliable packaging company ensures your items arrive safe and sound while presenting itself as the customer’s top choice compared to broken, crushed, or torn products.
Explore the Main Levels of Packaging
The three main levels of packaging are primary, secondary, and tertiary. Each level serves a different layer of protection while shipping products from one point to another. Let’s explore all levels in detail:
Primary Packaging – Protect the Product Directly
Simply, the type of packaging that protects or cushions the product directly is primary. Primary packaging basically serves as the main layer between the customer and the product. Usually, it protects the product when it is in use.
In other words, you can think of any packaging that comes in direct contact with the product as primary. Primary packaging preserves, contains, and protects the inside-packed contents. You would also find labels conveying essential information for customers, such as ingredients or any toxicity warnings.
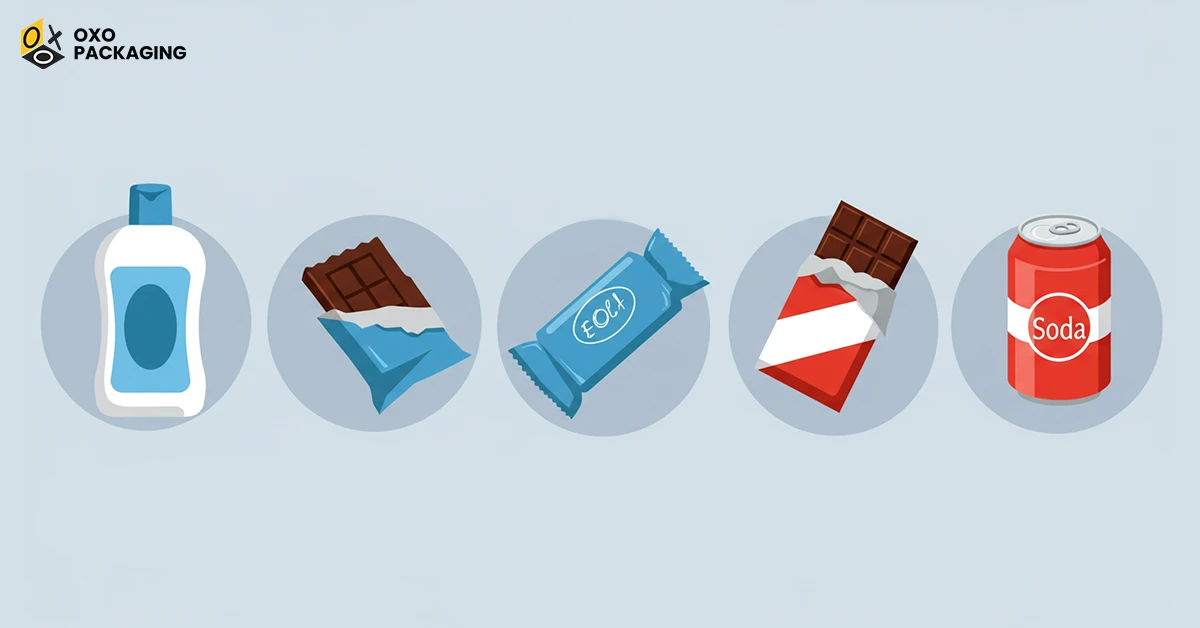

Examples of Primary Packaging
Multiple components are premium examples of primary packaging. For instance, a cosmetic lip gloss is housed in a tube-shaped bottle, which also contains a label and a lid. All components, including bottle, label, and lid, are primary packaging. Some other examples include:
- Protective film
- Glass bottles
- Protective plastic bags
- Glass jars
- Metal cans
- Tin cans
- Wrappers
- Skin packs
- Flexible pouches
- Blister packs
- Kraft paper around food items
Why Primary Packaging Matters?
The main objective of primary packaging is to hold, protect, and offer essential information about the product to customers. Hence, it should be designed to fulfil this objective effectively while enhancing visual appeal and brand identity to persuade customers and stand out in the market. Apart from this, primary packaging also serves best to effectively keep consumable and perishable products safe from contamination.
Important Considerations for Primary Packaging
Here are some top considerations for businesses that have a significant impact on product protection and user experience:
-
Product Compatibility
The packaging material must be compatible with your inside-packed contents to prevent reactions that can degrade the product or packaging quality. For example, acidic products may require specific barrier properties to avoid corrosion. However, food items may require packaging that is considered safe for consumables.
-
Product Protection
Primary packaging must effectively protect the product from harsh environmental factors like moisture, oxygen, and light that may degrade quality over time. Moreover, it should also offer physical protection to products from knocks and bumps during handling and shipping. Businesses should perform thorough testing to ensure the suitability of primary packaging for products.
-
Tamper Evidence
A wide range of products, especially in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, need packaging that must offer evidence if tampering has occurred. This can be acquired through the use of tamper-evident seals for your primary packaged products. Tamper-evident seals also prolong the shelf life of perishable items such as cookies, breads, and medicines.
-
Barrier Properties
Materials used in primary packaging need to have effective barrier properties to protect the product from various harmful elements. Gases, vapours, and liquids are among these elements. Keep in min that different products have different requirements for protection. For example, perishable items might need a high barrier against oxygen to prolong their shelf life.
-
Regulatory Compliance
There are certain regulations governing packaging materials depending on industry and the geographical location. Hence, packaging materials for food and pharmaceutical products must comply with safety standards set by regulatory bodies like the APCO in Australia or the FDA in the United States. Moreover, many toxic materials need UN-rated packaging to ensure safe handling and shipping.
-
Eco-Friendly Materials
Due to increasing awareness of environmental issues, choosing eco-friendly materials is a significant aspect to consider. These materials can be recyclable, biodegradable, or derived from renewable resources, while minimising carbon footprint and reducing negative environmental impact. This aspect attracts eco-aware customers as well as helps brands meet sustainability goals.
-
User-Friendly Packaging
Convenient packaging for the end user is crucial. Features like resealability, ease of opening, and the ability to dispense the product efficiently come under convenient packaging. Adopting these features enhances user experience while boosting customer satisfaction. Otherwise, you may compromise your brand image with difficult packaging design.
-
Budget-Friendly Option
While utmost protection of products while complying with packaging regulatory needs is important, a budget-friendly packaging solution is also essential. Hence, you should choose optimal material and production cost while filling process efficiently, and to reduce the shipping costs as much as you can. Lightweight packaging reduces shipping costs compared to heavier items.
-
Branding Opportunities
More likely, the primary packaging is often the first impression and physical interaction between your finished product and the customer. So, it must accurately reflect the image of your brand, attract your customers’ attention, and communicate essential information about your packaged product. Many brands use sleek finishes to highlight the logo and other graphic details.
-
Prolonged Shelf-Life
Choosing the right materials for packaging helps prolong a product’s shelf life by protecting against harsh environmental factors. This aspect is crucial for food products and pharmaceuticals, where the quality and protection of the product over time are vital. In crux, the right packaging materials preserve the integrity and quality of the product for a longer period.
Secondary Packaging – Enhanced Protection and Presentation
As the name indicates, the second layer of packaging for the product following the primary packaging is secondary packaging. Its main function is to provide additional product protection for transporting and storing products.
Hence, secondary packaging helps keep bulk products well-organised and offers an additional layer for branding and marketing by using printed graphics, text, and artwork on the packaging material. This packaging is often used in multiple industries like food, cosmetics, over-the-counter medications, and beverages.
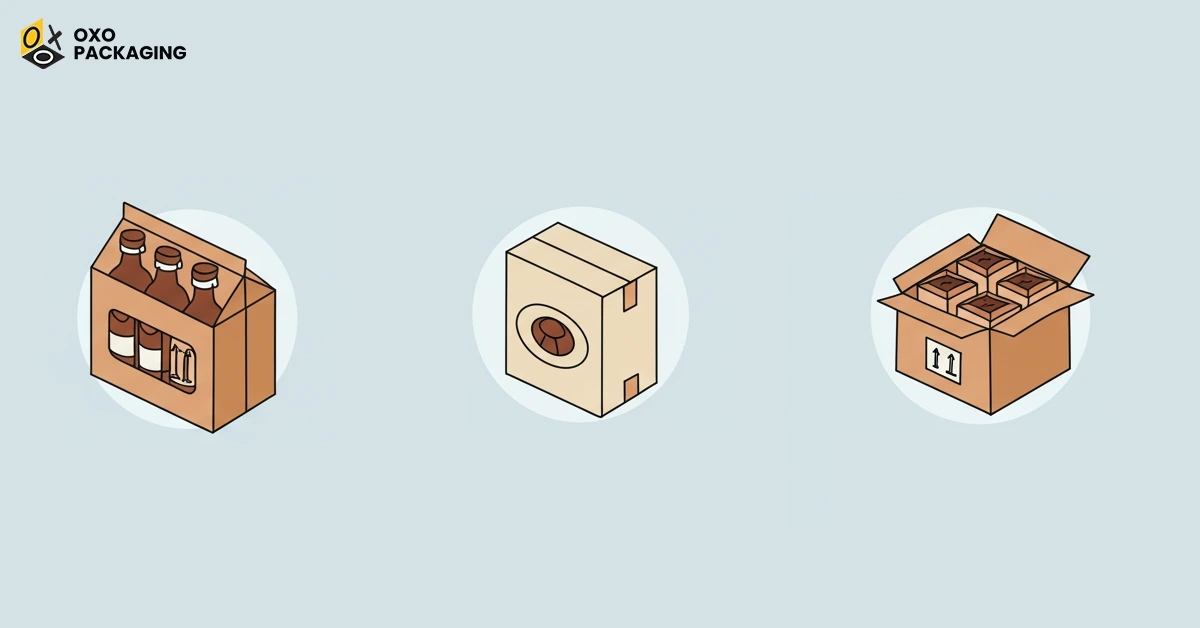
Examples of Secondary Packaging
Secondary packaging is usually the first point of contact between the customer and your product. For example, the box you see on the pharmacy shelf containing a pill bottle of medicine is secondary packaging. Other types of secondary packaging include:
- Pouches
- Plastic bags
- Paper packaging
- Bubble mailers
- Trays
- Cartons
- Paperboard boxes and other paperboard packaging
- Bubble wrap
- Gift packaging
Why Secondary Packaging Matters?
The main function of secondary packaging is to provide extra protection for primary packaging. Apart from this, this packaging level allows retailers to showcase products more persuasively and effectively for consumers to notice and buy as well. Secondary packaging basically serves as another place for branded messaging to be conveyed to customers. Renowned brands like Savoy and Jatz use shelf-ready secondary packaging boxes with powerful branding elements.
Important Considerations for Secondary Packaging
When considering the secondary packaging, here are some factors to consider to boost customer loyalty and engagement:
Environmental Impact: Can you choose an environmentally friendly material for this layer of your packaging?
-
Flexible Printing Material
Keep in mind to choose a packaging material that is easy to print on, where you can add marketing material and essential information to the customers. Screen, offset, digital, lithographic, and flexographic are popular printing options for secondary packaging.
-
High-Durable Material
Ensure you choose materials that are highly robust and can withstand shocks and vibrations during shipping. Durable material must be able to resist wear and tear while preserving the integrity of products.
-
Environmental Sustainability
If you choose eco-friendly packaging material for the secondary layer of your packaging, then you can create an ethical image of your brand. Environmentally friendly materials help brands attract eco-aware customers as well as support green credentials.
-
Moisture-Resistant
Your packaging material must resist moisture to prevent quality degradation of your product and packaging. Higher humidity levels lead to poor air quality, causing irritating odours, particles, and vapours. They can heavily degrade the quality, taste, and aroma of perishable items.
Tertiary Packaging – Ensure Safe Handling and Shipping
Most products in a modern retail environment have to be shipped at some point in time. That’s where tertiary packaging comes into play and offers protection to the products for safe handling and transit. Shipping containers, transit packaging, and boxes are used to ship products to retailers or consumers in tertiary packaging.
With durable and designed to group multiple products into one load for transport, tertiary packaging serves best. This packaging is not displayed to a customer unless the product is delivered directly to the customer.
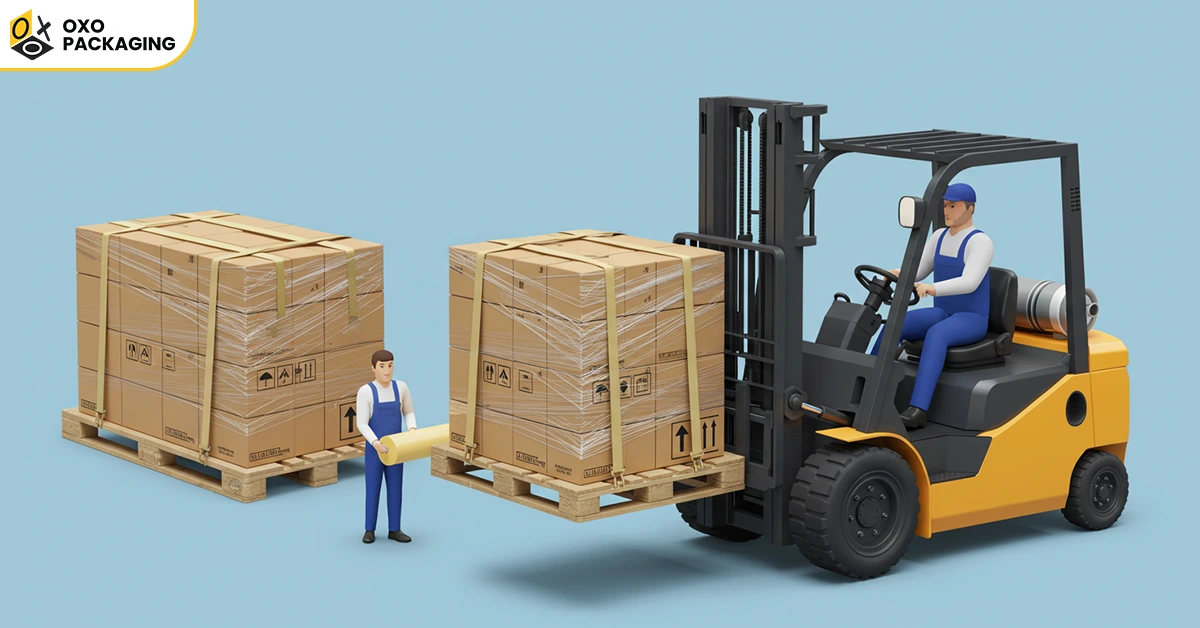

Examples of Tertiary Packaging
Anything used in shipping is considered tertiary packaging. Durability and intact packaging of products are premium features of this packaging. Some common packaging materials that are used in tertiary packaging include:
- Corrugated cardboard boxes
- Rigid boxes
- Wood pallets
- Stretch film and shrink film
- Shipping and transit containers
Why Tertiary Packaging Matters?
Tertiary packaging is crucial to hold products intact and pristine during shipping. This packaging offers extra protection to inside-packed products by encasing both primary and secondary packaging in the shipping process. Hence, it is significant for efficient logistics and product protection even during rough handling and shipping. The third level of packaging groups secondary packaging units while making them easier to handle, move, and store in bulk.
The primary function of tertiary packaging is holding products during shipping. It provides additional protection of the product by encasing the secondary and primary packaging in the transit process.
Important Considerations for Tertiary Packaging
Tertiary packaging includes primary materials such as wood, plastic, and cardboard. There are several factors to consider to help reduce your shipping costs. But the following factors are a good place to start:
-
Weight Considerations
Since most shipping involves weighing the product, considering the weight of the packaging will help make the process more affordable.
-
User-Convenience
Tertiary packaging requires to secondary units to be put together, filled, and closed for efficient shipping operations. Although tertiary packaging is not directly seen by consumers, it plays a significant role in overall user convenience by streamlining easier handling, storage, and transportation of products.
-
Sustainable Packaging
Allow your brand to reduce its carbon footprint by using recyclable materials, like paper-based materials or plant-based materials. Choose recycled, natural materials, such as paper pulp, over plastic to support environmental sustainability.
-
Right-Sized Packaging
Choose tertiary packaging tailored to the proper size of the inside packed contents. Doing so will reduce the weight of the shipping load and waste accumulation. Remember that tertiary packaging comes in all different shapes to hold your goods accurately.
How To Determine the Right Packaging for Each Product?
Choosing the right packaging for your products is not as simple as it seems. Several factors, from legal compliance to branding opportunities and buying decisions, play a crucial role. To determine the most suitable packaging level, your brand evaluates these factors:
- Keep in consideration the size and weight of your product. Select a packaging option that will safeguard the product while adding the minimal weight to it as possible.
- Choose a suitable environment where the product will be stored or used while ensuring the packaging will keep the product protected. For example, if you have a high-humidity environment, you should use plastic or glass instead of cardboard to protect the product.
- Examine the product you want to package. And consider what risks exist that would harm the integrity of your product? Opt for packaging that will protect against this risk.
- Observe consumer needs and design tailored packaging. Choose accessible containers that are easy to open or eco-friendly materials.
- Consider shipping choices and dynamics to hold up your packaging products under particular type of shipping.
- Think about your budget. Packaging can come in a variety of prices, so choose a packaging material that complements your budget while meeting your other brand needs.
Choose the Right Packaging Supplier to Boost Brand Recognition

Having so many considerations to make when choosing the right packaging levels and materials for your product can’t be taken lightly. As they directly impact the quality of your product, as well as customer perception about your brand. So, working with a reliable packaging supplier that understands packaging and all of its options is crucial.
From providing the best packaging solutions to optimise your budget and goals to creating custom packaging designs that perfectly fit your product and brand identity, the OXO Packaging team is here to help you make these important packaging decisions. Contact us today to learn more about our custom packaging options.
The most common packaging level includes:
- Primary Packaging (Consumer Packaging)
- Secondary Packaging (Retail Packaging)
- Tertiary Packaging (Transit/Bulk Packaging)
The utilization of the packaging levels depends on the shopping needs. For retail purposes, the second level may be enough to cater to the demands. While for huge volumes, going without the tertiary packaging isn't feasible.
Financially, this may increase the cost, but the movement of finished goods is not possible without it at bulk scale. Suppose the glass beverage bottles get damaged due to the absence of tertiary packaging. This unfortunate cost is much higher than the actual packaging costs that are meant to provide a secure solution.
